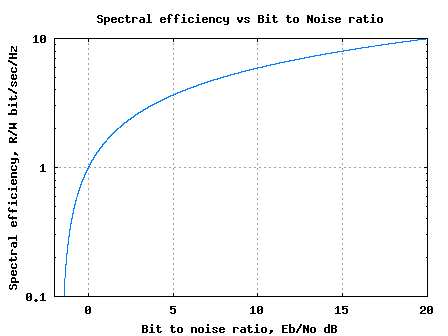
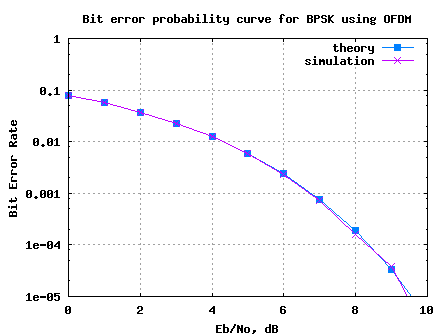
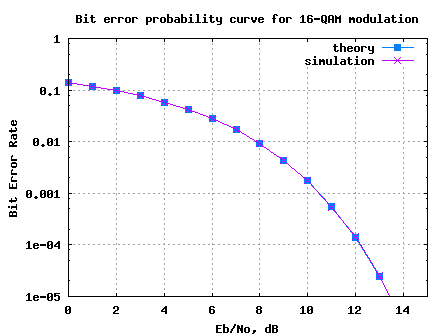
On July30th, 2008 I had sent a request for feedback to 93 subscribers who have opted to receive articles over email. As on 3rd August, I received the response from around 8 persons. Not bad, around 8.5% response. Thanks a lot for the feedback. I will summarize the response from the group and note down the action items on me.
Best in [dspLog]
The majority of the people (6) found the theoretical description to be the most useful and around 3 people found the Matlab/Octave code to be the most useful. A comment came from Mr. Eddie Maalouf who suggested that we should start encourage user participation where other engineers can help to solve technical problems etc.
Continue reading “Summary – feedback on [dspLog], July 2008”