As on 21st October 2007, we moved from blogspot domain at to the self hosted domain at https://dsplog.com. Over the last two years, the blog has grown quite a bit, and am reasonably happy with the progress. Let us look back at the positives and negatives over the last year.
Quiz on IEEE 802.11a specifications
The IEEE 802.11a specifications are used by many to understand a wireless communication link built using OFDM. In this post, I have put together a set of 10 multiple choice questions based on 802.11a specifications. The questions are on the building blocks in 802.11a specifications, preamble structure and so on. Upon completion of the quiz, you will be lead to a page showing the correct answers and their explanations.
Click here to download IEEE 802.11a specifications.
Note: The quiz might not be visible on RSS reader or over email. Please visit the site to access the quiz.
Good luck!
[QUIZZIN 4]
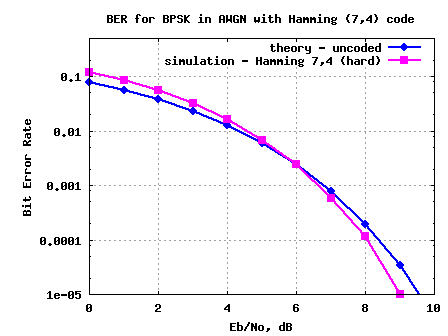
Hamming (7,4) code with hard decision decoding
In previous posts, we have discussed convolutional codes with Viterbi decoding (hard decision, soft decision and with finite traceback). Let us know discuss a block coding scheme where a group of information bits is mapped into
coded bits. Such codes are referred to as
codes. We will restrict the discussion to Hamming
codes, where 4 information bits are mapped into 7 coded bits. The performance with and without coding is compared using BPSK modulation in AWGN only scenario.
Continue reading “Hamming (7,4) code with hard decision decoding”
OCW: Communication System Design
While browsing through the web for materials on the wireless communication and implementation, found this rich set of articles as part of MIT OPEN COURSEWARE program. The course is from Vladimir Stojanovic, course materials for 6.973 Communication System Design, Spring 2006. MIT OpenCourseWare (http://ocw.mit.edu/), Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Matlab or C for Viterbi Decoder?
Are you bothered by speed of the speed of the simulations which you develop in Matlab/Octave? I was not bothered much, till I ran into the Viterbi decoder. If you recall, the Matlab/Octave simulation script for BER computation with hard soft decision Viterbi algorithm provided in post Viterbi with finite survivor state memory took around 10 hours to run.
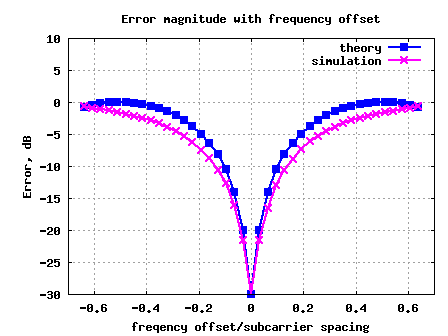
Inter Carrier Interference (ICI) in OFDM due to frequency offset
In this post, let us evaluate the impact of frequency offset resulting in Inter Carrier Interference (ICI) while receiving an OFDM modulated symbol. We will first discuss the OFDM transmission and reception, the effect of frequency offset and later we will define the loss of orthogonality and resulting signal to noise ratio (SNR) loss due to the presence of frequency offset. The analysis is accompanied by Matlab/Octave simulation scripts.
Continue reading “Inter Carrier Interference (ICI) in OFDM due to frequency offset”
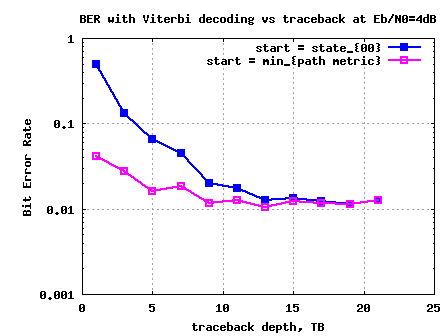
Viterbi with finite survivor state memory
In the post on Viterbi decoder and soft input Viterbi decoder, we discussed a convolutional encoding scheme with rate 1/2, constraint length and having generator polynomial
and having generator polynomial
. If the number of uncoded bits is
, then the number of coded bits at the output of the convolutional encoder is
. Decoding the convolutionaly encoded bits by Viterbi algorithm consisted of the following steps.
Continue reading “Viterbi with finite survivor state memory”
Softbit for 16QAM
In the post on Soft Input Viterbi decoder, we had discussed BPSK modulation with convolutional coding and soft input Viterbi decoding in AWGN channel. Let us know discuss the derivation of soft bits for 16QAM modulation scheme with Gray coded bit mapping. The channel is assumed to be AWGN alone.
Support Vibha’s Dream Mile event
My friend Mr. Balaji volunteers for Vibha, a non-profit organization whose mission is to ensure that every underprivileged child attains his or her right to education, health and opportunity.
Vibha, which was founded in 1991 has a volunteer network of 825 members spread across Atlanta, Austin, Bay Area, Boston, Chicago, Dallas, Houston, Jacksonville, Los Angeles, Milwaukee, Twin Cities – Minnesota, New York, Philadelphia, Sacramento, Washington DC and several other cities across the US and India. Till date, we have supported about 190 projects in India and the US. You may read more about their projects here.
To support Vibha’s cause, Mr Balaji has set up a donation page – The Dream Mile … A few miles for a million dreams . The Dream Mile 5k/10k Run/Walk is Vibha’s flagship event for increasing awareness and raising funds to help underprivileged children. Vibha has chosen My New Red Shoes as one of the beneficiaries of this event.
To find out more about My New Red Shoes, please watch the video below.
To find out more about Alamb, a project by Vibha in India, please watch the video below.
If you like some of the work done by Vibha, please consider making a donation to the cause. As Mr. Balaji has mentioned:
$120 can provide education to a child for a whole year
$50 can facilitate the rehabilitation of a mentally handicapped child for a year
$40 can sponsor the non-formal education of a child for a whole year.
To donate for this cause, please visit the donation page The Dream Mile … A few miles for a million dreams
Thanks again for your support.
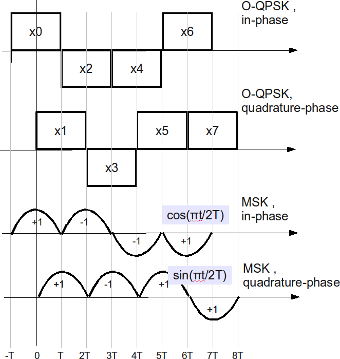
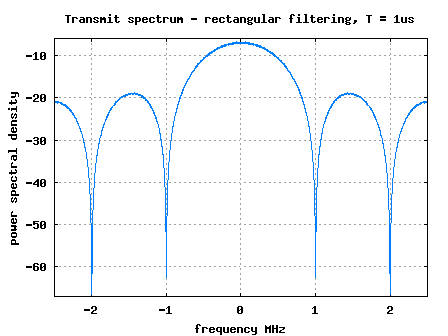
MSK transmitter and receiver
In a post on Minimum Shift Keying (MSK), we had discussed that MSK uses two frequencies which are separated by and phase discontinuity is avoided in symbol boundaries. In that post, we had discussed MSK as a continuous phase transmit signal and showed that phase changes through 0, 90, 180 and 270 degrees. In this post, we will discuss MSK transmission as a variant of offset-QPSK technique. Further, we will discuss the receiver structure and show that bit error rate with coherent demodulation of MSK (using
time) is equivalent to that of BPSK modulation. The channel assumed is AWGN.
Solved objective questions (GATE)
Using the services of a new author ‘RV’, we are starting a new series of articles in the blog. Typically in India, many of the competitive examinations pertaining to Engineering (GATE, IES) and rectuitment by private and public sector companies (ISRO, BSNL, BEL, BHEL) uses examination with objective questions for the first level screening. We are hoping that this Objective Question Answer series, mostly discussing topics pertaining to Electronics and Communication Engineering, will help those preparing for those examination. Kindly do give your feedback via comment and/or email. Thanks, Krishna
Continue reading “Solved objective questions (GATE)”
BER with Matched Filtering
In the post on transmit pulse shaping filter, we had discussed pulse shaping using rectangular and sinc. In this post we will discuss about optimal receiver structure when pulse shaping is used at the transmitter. The receiver structure is also called as matched filter. For the discussion, we will assume rectangular pulse shaping, the channel is AWGN only and the modulation is BPSK.
Continue reading “BER with Matched Filtering”
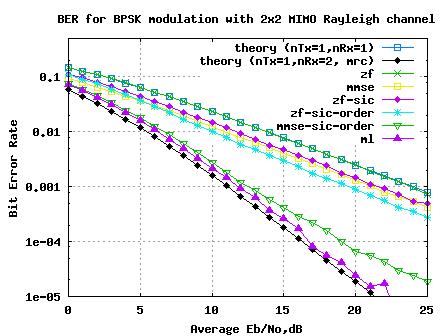
Six equalizers for V-BLAST
In the past, we had discussed several posts on two transmit two receive MIMO communication, where the transmission was based on V-BLAST. The details about V-BLAST can be read from the landmark paper V-BLAST: An architeture for realizing very high data rates over the rich scattering wireless channel – P. W. Wolniansky, G. J. Foschini, G. D. Golden, R. A. Valenzuela. We will assume that the channel is a flat fading Rayleigh multipath channel and the modulation is BPSK.
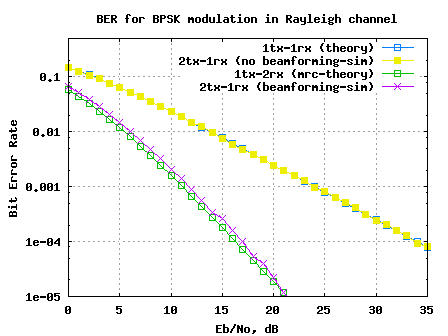
Transmit beamforming
In this post lets discuss a closed-loop transmit diversity scheme, where the transmitter has the knowledge of the channel. As there is a feedback path required from the receiver, to communicate the channel seen by the receiver to the transmitter, the scheme is called closed-loop transmit diversity scheme. Recall that the transmit diversity using Space Time Coding (Alamouti STBC) does not require the knowledge of the channel. In this post, we will restrict our discussion to a 2 transmit, 1 receive case. We will assume that the channel is a flat fading Rayleigh multipath channel and the modulation is BPSK.