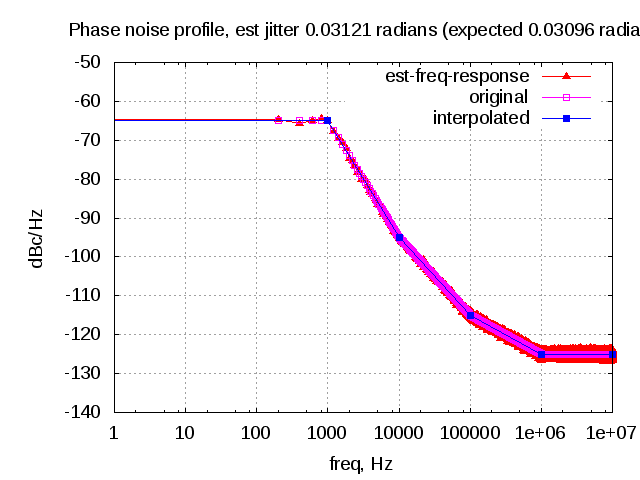
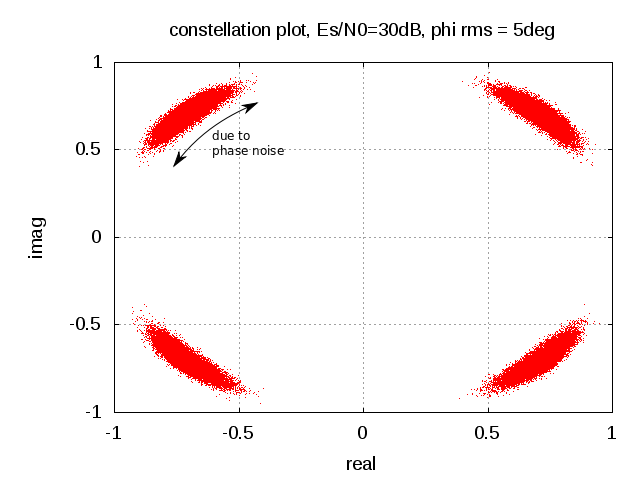
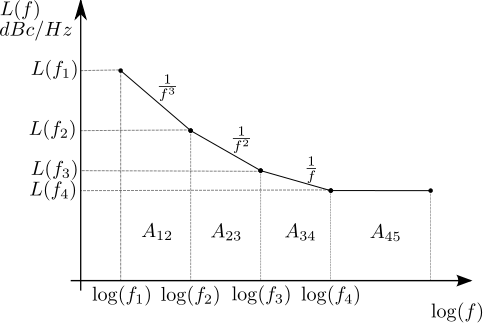
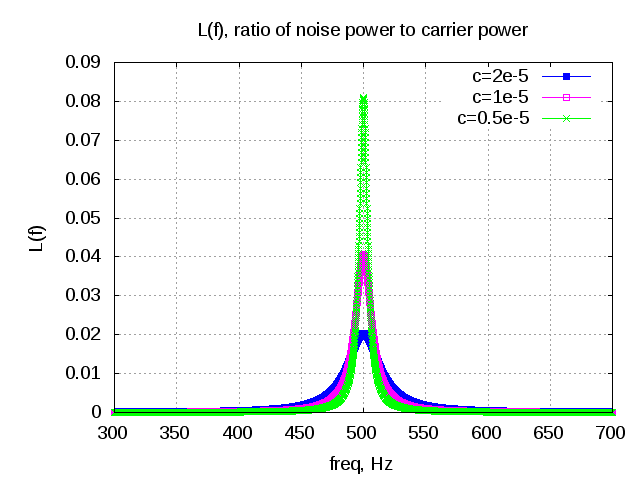
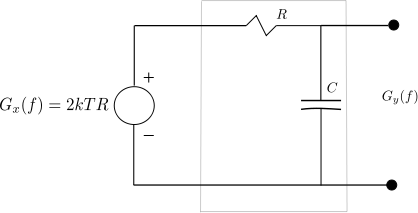
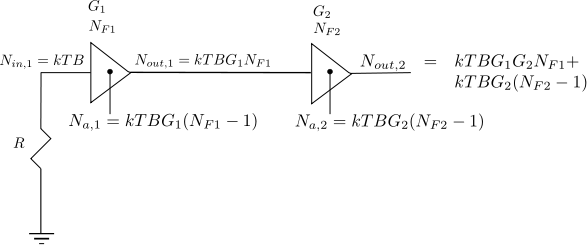
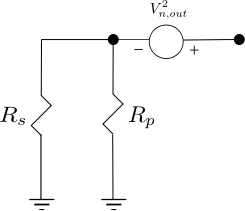
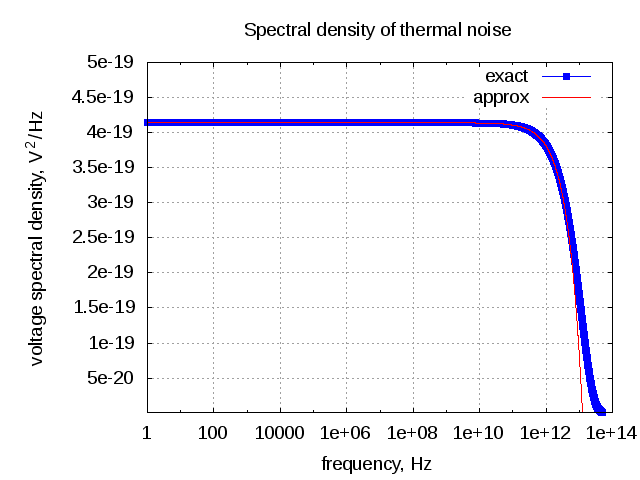
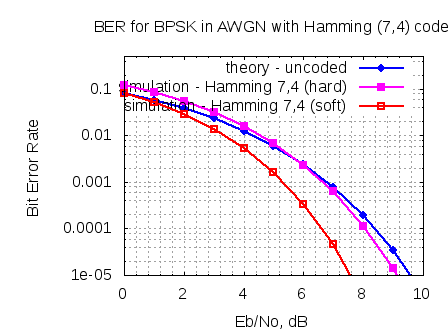
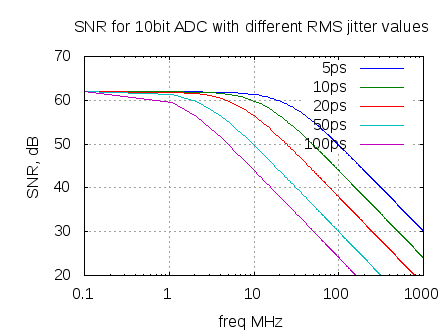
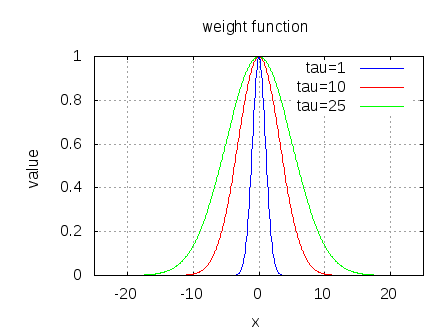
In typical wireless system simulations, there is a need to model the phase noise profile of the local oscillator. For eg, the phase noise profile of the oscillator can be of the shape described in the post on Phase Noise Power Spectral Density to Jitter. While looking around for example Matlab code, found two references [1, 2] which uses the approach of defining the phase noise profile in frequency domain, and then using ifft() to convert to the time domain samples. This post gives a brief overview of the modeling and provides an example Matlab/Octave code.
Continue reading “Modeling phase noise (frequency domain approach)”