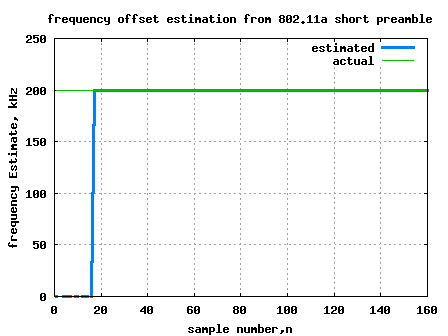
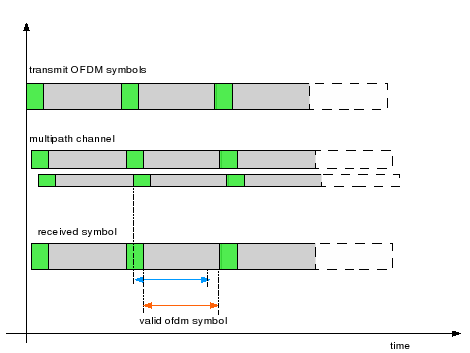
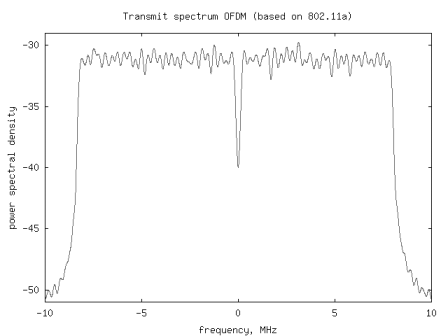
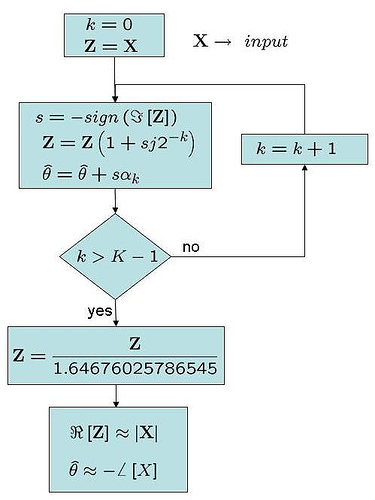
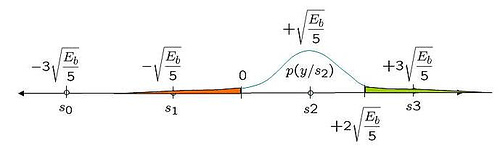
From the previous post on OFDM (here), we have understood that an OFDM waveform is made of sum of multiple sinusoidals (also called subcarriers) each modulated independently. In this post, let us try to understand the estimation of frequency offset in a typical OFDM receiver (using the short preamble specified per IEEE 802.11a specification as a reference).
Understanding frequency offset
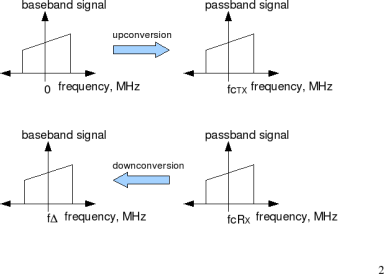
In a typical wireless communication system, the signal to be transmitted is upconverted to a carrier frequency prior to transmission. The receiver is expected to tune to the same carrier frequency for downconverting the signal to baseband, prior to demodulation.
Figure: Up/down conversion
Continue reading “Frequency offset estimation using 802.11a short preamble”