Question 15 on communication from GATE (Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering) 2012 Electronics and Communication Engineering paper.
Q15. A source alphabet consists of N symbols with the probability of the first two symbols being the same. A source encoder increases the probability of the first symbol by a small amount  and decreases that of the second by
and decreases that of the second by  . After encoding, the entropy of the source
. After encoding, the entropy of the source
(A) increases
(B) remains the same
(C) increases only if N=2
(D) decreases

Solution
Entropy of a random variable is defined as ,
.
Refer Chapter 2 in Elements of Information Theory, Thomas M. Cover, Joy A. Thomas (Buy from Amazon.com, Buy from Flipkart.com)
Let us consider a simple case where can take two values 1 and 0 with probability
and
respectively, i.e.
.
The entropy of is,
.
The plot of the entropy versus the probability is shown in the figure below.
clear all; close
p = [0:.001:1];
hx = -p.*log2(p) - (1-p).*log2(1-p);
plot(p,hx);
xlabel('probability, p'); ylabel('H(X)');
title('entropy versus probability, p');
axis([0 1 0 1]);grid on;
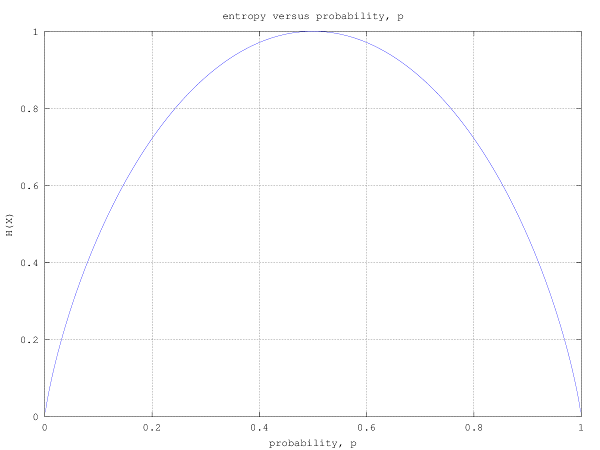
Figure : Entropy versus probability for binary symmetric source
It can be see that the entropy (also termed as uncertainty) is maximum when and for other values of
, the entropy is lower. The entropy becomes 0 when
i.e. when the value of
becomes deterministic. If we extend this to a source with more than two symbols, when probability of one of the symbols becomes more higher than the other, the uncertainty decreases and hence entropy also decreases.
Based on the above, the right choice is (D) decreases
References
[1] GATE Examination Question Papers [Previous Years] from Indian Institute of Technology, Madras http://gate.iitm.ac.in/gateqps/2012/ec.pdf
[2] Elements of Information Theory, Thomas M. Cover, Joy A. Thomas (Buy from Amazon.com, Buy from Flipkart.com)